Back to Course
CoM SSA Sustainable Energy Access and Climate Action Plan (SEACAP) course
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
MODULE 1: Setting the scene
-
Lesson 1.1: Introduction to the CoM SSA initiative2 Topics
-
Lesson 1.2: Introduction to the SEACAP3 Topics
-
Lesson 1.3: Climate change and cities in Africa2 Topics
-
MODULE 2: SEACAP mitigation pillar
-
Lesson 2.1: Key concepts in climate change mitigation1 Topic
-
Lesson 2.2: Introduction to the mitigation pillar2 Topics
-
Lesson 2.3: The SEACAP development process for the mitigation pillar1 Topic
-
Lesson 2.4: Emissions inventories: GHG emissions4 Topics
-
Lesson 2.5: Developing a Baseline Emissions Inventory (BEI)3 Topics
-
Lesson 2.6: Tools for BEI development2 Topics
-
MODULE 3: SEACAP access to energy pillar
-
Lesson 3.1: Key concepts in access to energy
-
Lesson 3.2: Introduction to the access to energy pillar2 Topics
-
Lesson 3.3: The SEACAP development process for the access to energy pillar
-
Lesson 3.4: Data collection3 Topics
-
Lesson 3.5: Developing an Access to Energy Assessment (AEA)2 Topics
-
Lesson 3.6: Setting an energy vision and targets3 Topics
-
Module 3.7: Planning energy actions3 Topics
-
MODULE 4: SEACAP adaptation pillar
-
Lesson 4.1: Key Concepts in climate change adaptation1 Quiz
-
Lesson 4.2: Introduction to the adaptation pillar2 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Lesson 4.3: The SEACAP development process for the adaptation pillar1 Topic|1 Quiz
-
Lesson 4.4: Developing a Risk and Vulnerability Assessment (RVA)1 Quiz
-
Lesson 4.5: Setting an adaptation vision and sectoral targets2 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Lesson 4.6: Planning adaptation actions2 Topics|1 Quiz
-
MODULE 5: Steps to take before you implement your SEACAP
-
Lesson 5.1: Next steps for prioritised actions
-
Lesson 5.2: Categorising actions to access external finance2 Topics|1 Quiz
-
MODULE 6: Communicating your SEACAP
-
Lesson 6.1: Designing your SEACAP3 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Lesson 6.2: Communicating your SEACAP to key stakeholders1 Topic|1 Quiz
-
MODULE 7: Reporting your SEACAP
-
Lesson 7.1: Introduction to reporting your SEACAP3 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Lesson 7.2: Introduction to reporting the mitigation pillar4 Topics|1 Quiz
-
MODULE 8: Integrating your SEACAP into existing planning processes
-
Lesson 8.1: Integrating your SEACAP actions into local level plans1 Topic
-
Lesson 2.7: Setting mitigation targets2 Topics
-
Lesson 2.8: Planning mitigation actions1 Topic
-
Lesson 7.4: Introduction to reporting the access to energy pillar3 Topics
-
Lesson 7.3: Introduction to reporting the adaptation pillar3 Topics
Participants 1632
Lesson 16, Topic 2
In Progress
Data collection tools in the SEACAP development toolbox
3 October 2024
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
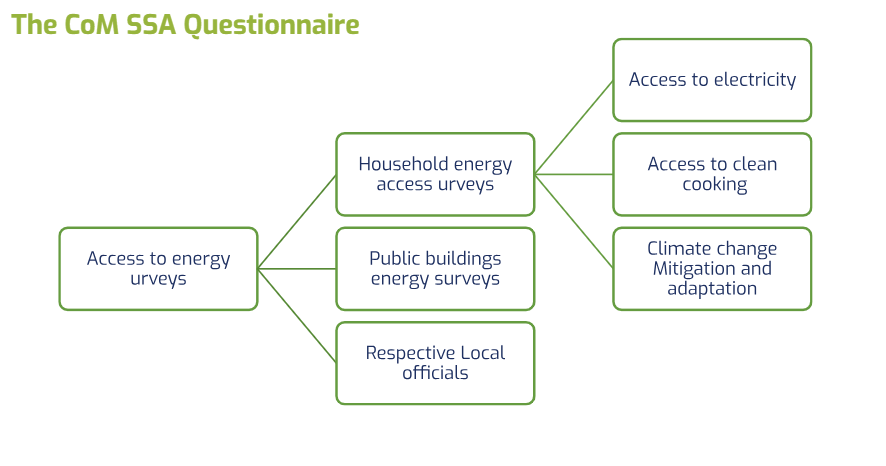
Data collection tools include:
- Excel-based Access to Energy Questionnaire
- Digitised access to energy questionnaire – KoBo Toolbox
- A data collection guide for enumerators and supervisors
- Others: consent form, NDA, interview tracking form
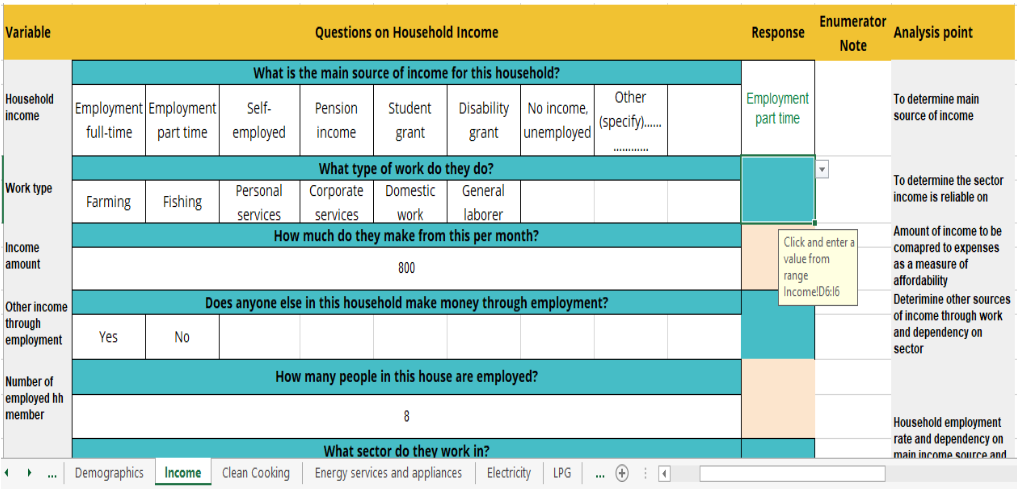
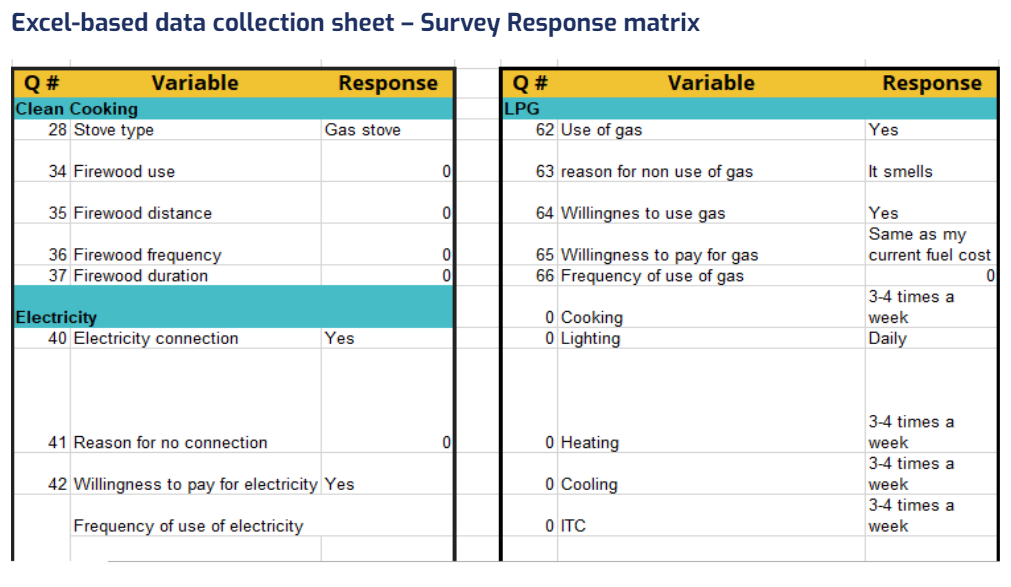
Excel-based data collection sheet
–This contains sheets on:
- Income,
- Demographics
- Clean cooking
- Electricity, LPG
- Mitigation, etc.
- and a response matrix
Digital data collection: Using KoBo Toolbox
KoBoToolbox overview:
- Ability to create, record, collect and analyse data
- No internet connection required during data collection
- Data can be collected using internet browser or KoBo Collect on Android devices
- Ability to use browser or Android data collection app
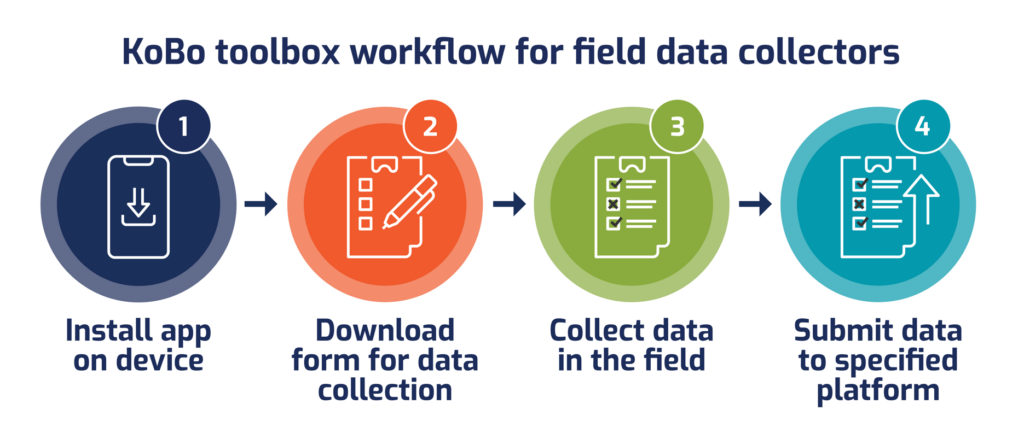
KoBo Toolbox sample questions in the digital KoBo questionnaire
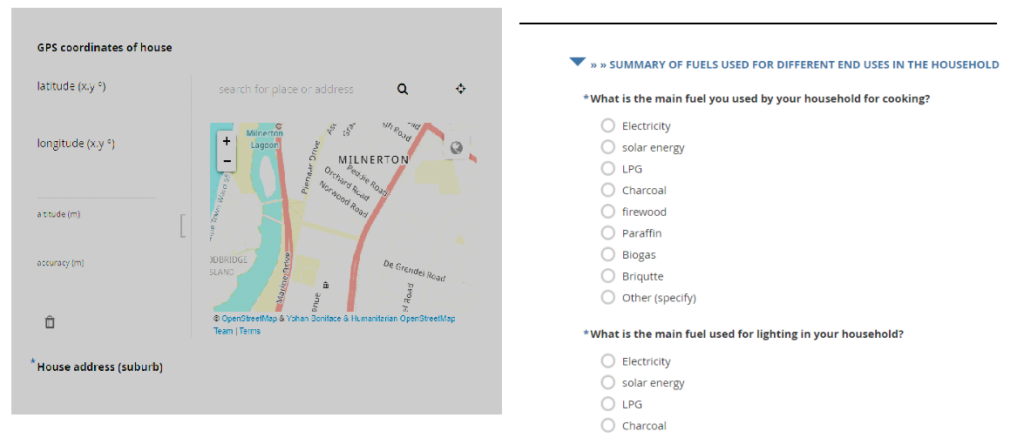
KoBo toolbox data collection results
Results can be viewed as:
- Reports
- Tables
- Gallery
- Downloads
- Maps
Best practices for data collection:
- Check data as it is coming in (get data in real time).
- Decide who will be responsible for data cleaning.
- Request back-check permission at the end of an interview (get phone numbers).
- Develop questions for result (quality checks).
Other data sources
There are other data sources for the access to energy pillar of the SEACAP. Here are some tips:
- Local data is ideal.
- Choose national data in the absence of local data (from public institutions).
- Try international organisations such as the FAO, IEA, IRENA.
- Use online platforms such as the climate information platform of CSAG.
- Collaboration with universities is another helpful option.
- You could try data scaling: e.g. by comparing population or number of petrol stations.
What happens after data collection?
- Data is cleaned. and analysed.
Data cleaning is a vital step, and various tools can be used:
- Stata
- Python
- Excel
- Back-checking with respondents takes place.
- Data is analysed.
